Home > Technical & Training > O Techniques
Competition Rules
Foot Orienteering
International orienteering competitions is organised as according to the Rules of International Orienteering Federation. Other than specific rules set by local organisation, all orienteering competitions around the world refers to the same Rules.
Competitions in Hong Kong abide by the Orienteering Competition By-Laws of Orienteering Association of Hong Kong.
IOF World Class Events Organiser's Guidelines > Links to IOF guidelines
International orienteering competitions is organised as according to the Rules of International Orienteering Federation. Other than specific rules set by local organisation, all orienteering competitions around the world refers to the same Rules.
Competitions in Hong Kong abide by the Orienteering Competition By-Laws of Orienteering Association of Hong Kong.
IOF World Class Events Organiser's Guidelines > Links to IOF guidelines
Trail Orienteering
In trail orienteering competition, the International Orienteering Federation published the IOF TrailO Rules 2020.
IOF also published guidelines for organizing TrailO events and Technical Introduction to TrailO for Experienced Foot Orienteers.
> Framework for TrailO Competitions issued by Orienteering Association of Hong Kong (in Chinese only)
In trail orienteering competition, the International Orienteering Federation published the IOF TrailO Rules 2020.
IOF also published guidelines for organizing TrailO events and Technical Introduction to TrailO for Experienced Foot Orienteers.
> Framework for TrailO Competitions issued by Orienteering Association of Hong Kong (in Chinese only)
Other Codes & Policies
> Code of Practice – Conservation of The Environment
> Anti-Doping Policy of Orienteering Association of Hong Kong
> Code of Practice – Conservation of The Environment
> Anti-Doping Policy of Orienteering Association of Hong Kong
Orienteering Map Symbols
International Orienteering Federation standard orienteering map symbols applies in all orienteering competition around the world:
ISOM 2017-2 was effective in January 2019, which will superseded the ISOM 2017.
> ISOM 2017-2 (Jan 2019 edition)
> ISOM 2017-2 (Sep 2022 5th Revision edition)
> Differences between ISOM 2000 and ISOM 2017 (IOF)
ISSprOM 2019 for sprint orienteering will be effective on 1/1/2019.
> ISSprOM 2019 (Apr 2019 edition)
> ISSprOM 2019-2 (Sep 2022 5th Revision edition)
> Guidelines for Mapping and Course Planning in Complex Urban Structures on Sprint Orienteering Maps 2022-01-23
ISOM 2017-2 was effective in January 2019, which will superseded the ISOM 2017.
> ISOM 2017-2 (Jan 2019 edition)
> ISOM 2017-2 (Sep 2022 5th Revision edition)
> Differences between ISOM 2000 and ISOM 2017 (IOF)
ISSprOM 2019 for sprint orienteering will be effective on 1/1/2019.
> ISSprOM 2019 (Apr 2019 edition)
> ISSprOM 2019-2 (Sep 2022 5th Revision edition)
> Guidelines for Mapping and Course Planning in Complex Urban Structures on Sprint Orienteering Maps 2022-01-23
IOF Mapping Standard Colour Test Chart
> Print Test Sheet OCAD 11
> Instruction
> IOF Printing Colour Standard
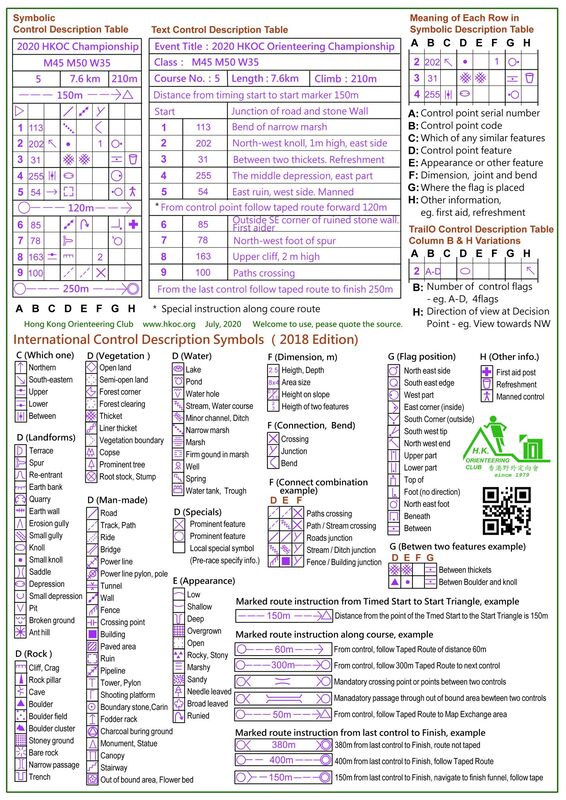
Orienteering Control Description Symbols
Orienteering in Hong Kong and many major orienteering competition adopt the International Orienteering Federation standard control description symbols (Apr, 2018 edition).
IOF Control Description Sheet Sample (2018) > Download
IOF Control Description Sheet Sample (2018) > Download
Orienteering Technical Training Exercises
The followings are common exercises that can be found in orienteering technical training and practice events.
* Source of demonstration map in this section from O-training.net.
* Source of demonstration map in this section from O-training.net.
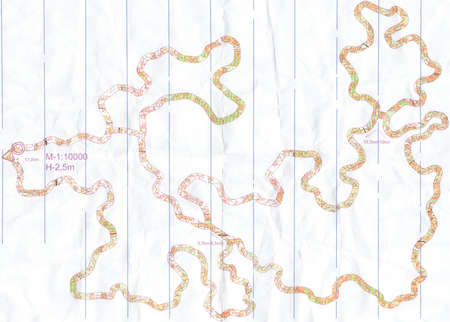
Brown Map
|
This is a exercise with use of a map that only shows the brown colour terrain features of an orienteering map, that is only with contour lines and other terrain features. The orienteer must focus on the contours in orienteering as this is the only information on the map. This exercise reinforce contour line reading ability and concentration. Without any display of runnability of vegetation, this is more appropriate to have a fairly open forest terrain to do a brown map exercise. There may add on information of some obvious impassable features and key locating features for orienteer with less experience.
|
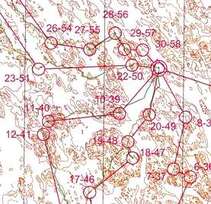
Corridor Orienteering
|
This exercise use a map that only show the map details in a narrow strip corridor of 50-100 m wide on ground. Other area outside the corridor is blank on map. The orienteer needs to stay inside the corridor during navigate through, with use of control points or GPS to verify how far the orienteer can stay within the corridor. With a course with control points along the route make the training more interesting. This exercise train the detail map reading of fine details that may not be used in normal orienteering.
|
Line Orienteering
|
This exercise requires the orienteer to run along a route as show on a line marked on the map. If the orienteer can maintain along the route on ground the orienteer will find the the control point or verify the accuracy with a GPS to trace back the actual route of running. The exercise train on accuracy of detail map reading. The difficulty of this exercise can be adjusted by varying the terrain, the intensity etc. go through for different skill levels of orienteer.
|
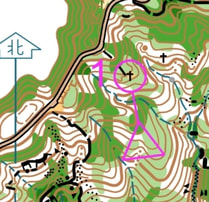
Map Memory
|
This exercise require the orienteer run without a map. The route ahead to the next control points must be memorized before leaving to next control. This train an orienteer on map reading skill on selecting key features from a map for navigation ahead and memorising it. Map example is from a HKOC practice event.
|
Traffic Light Orienteering
|
Before starting a normal orienteering course, plan ahead the route into three sections of green light - amber light - red light. Green light is the section that can run fast without too much attention on terrain details until arrive a point of an obvious feature. Then in the amber light section where require some attention in terrain features to prepare for approaching to the control point when arrive an attack point to the control. Finally, in the red light section area a fine orienteering require detail attention and slow down in order to find the control point. This is a good exercise to train a variation of navigation concentration and speed control and it is a common technique to be used in orienteering competition.
|
Window Orienteering
|
Similar to Corridor Orienteering, this exercise use map shows only the area around the control points,other area is blank on map. Area between two control points are hidden or shaded. The orienteer needs to run in straight line to the next control. This training ensure the orienteer with very good bearing running and cross country ability.
Map example is from a HKOC practice event. |